

The desire for TCR repertoire profiling in a variety of diseases and the advantages of a DBS-based method prompted us to establish a DBS-based TCR repertoire profiling method. Second, it is low cost and convenient to handle in that the filter cards can be stored and shipped at room temperature without refrigeration for at least 1 month.

#IMMUNE REPERTOIRE CAPTURE PROFESSIONAL#
First, it is minimally invasive (requiring only 0.3 mL of capillary blood obtained by finger- or ear-prick) and a field-friendly alternative to venipuncture by professional medical staff. There are two major advantages of this method. However, the costs, participant burden, regulatory constraints, and logistics associated with venipuncture and RNA handling are major barriers to clinical application or community-based research on various diseases.ĭry blood spots (DBS) have been used broadly in disease screening, drug level monitoring, and infectious microorganism detection, such as the detection of HIV and plasmodium. For TCR repertoire assessment, the current standard sample type is total RNA extracted from whole blood by venipuncture. There are different TCR library preparation for NGS, including: multiplex PCR, targeted enrichment methods, 5′Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (5′RACE) cDNA synthesis, template-switch, and nested PCR. Rapid progress has been made in the deep profiling of TCR repertoires by using NGS to discover millions of sequences from the TCR repertoires. Analyzing the TCR repertoire may help to gain a better understanding of the immune system features and of the etiology and progression of diseases, in particular those with unknown antigenic triggers. TCR repertoires of patients were explored in a variety of disorders-patients under cancer immunotherapy, autoimmune disease, or subject to virus infection (hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)). However, the complexity of the immune system in combination with the limitation of detection methods makes this subject difficult to research.Ĭurrently, TCR repertoire sequencing is widely used to evaluate the immune system. The advantage of immunotherapy in cancers has led to increasing numbers of studies dedicated to exploring the impact and interaction between immunity and cancer cells. Immunology research, particularly next generation sequencing (NGS) of the immune T-cell receptor β (TCRβ) repertoire, has advanced progression in several fields including treatment of various cancers and autoimmune diseases. The system is sensitive to low RNA input, and the results are highly correlated with whole blood uCDR3 discovery allowing study scale-up to better understand the relationship and mutual influences between the immune and diseases.
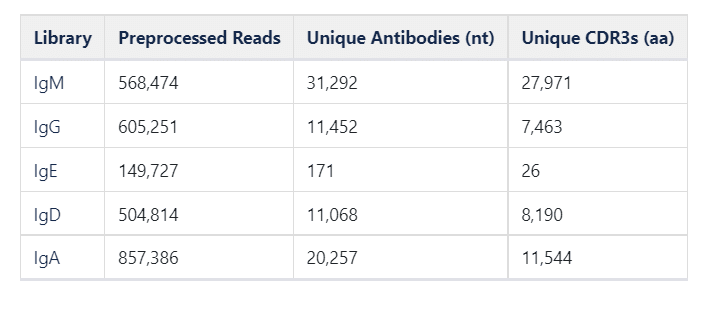
The DBS-based TCR repertoire profiling method is minimally invasive, provides convenient sampling, and incorporates fully automated library preparation. A low rate of clonotype sharing, 0.03–1.5%, was found among different individuals. About 74–90% of top 50 uCDR3 clones of whole blood could also be detected from DBS. uCDR3 discovery was neither affected by storage temperatures (room temperature versus − 20 ☌) nor storage durations (1, 14, and 28 days) when compared to whole blood. According to the statistical analysis and laboratory confirmation, 40 of 2-mm punch disks from the filter cards were enough to detect the shared top clones and have strong correlation in the uCDR3 discovery with whole blood. We demonstrated that the dominant clonotypes from the DBS results recapitulated those found in whole blood. RNA was extracted from DBS of the filter card, and fully automated multiplex PCR was performed to generate a TCRβ chain library for next generation sequencing (NGS) analysis of unique CDR3s (uCDR3). Methodsįinger-prick blood was collected onto a Whatman filter card. This study aimed to identify the TCR repertoires from dry blood spots (DBS), a method that will help collecting real-world data for biomarker applications. Immunology research, particularly next generation sequencing (NGS) of the immune T-cell receptor β (TCRβ) repertoire, has advanced progression in several fields, including treatment of various cancers and autoimmune diseases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
